1、推箱子
题目:
给你一个矩阵,里面有‘#’,表示障碍,‘.’表示空地,‘S’表示人开始的位置,‘E’表示箱子的预期位置,‘0’表示箱子的初始位置,你的任务是把箱子从‘0’推到‘E’.
注意不能将箱子推到‘#’上,也不能将箱子推出边界;
现在给你游戏的初始样子,你需要输出最少几步能够完成游戏,如果不能完成,则输出-1.
输入描述:
第一行为2个数字,n,mn,m,表示游戏盘面大小有nn行mm列(5<n,m<505<n,m<50);后面为nn行字符串,每行字符串有mm字符,表示游戏盘面.
输出描述:
一个数字,表示最少几步能完成游戏,如果不能,输出-1.
样例输入:
3 63 6
.S#..E.S#..E
.#.0...#.0..
............
样例输出:
1111
解析:
首先可以看出是一个bfsbfs问题,推箱子的时候首先人要站到箱子紧挨的四个方向的格子中,才能把箱子推向某一个方向,因此,两个bfsbfs,第一个bfsbfs搜索箱子的位置,第二个bfsbfs搜索人的位置到箱子紧挨的四个方向的格子要走的步数,大致方向就是这样,下面说下细节.
到终点时,箱子可以从四个方向推到终点,因此要维护一个最小值,当然了,箱子可能并不一定可以从四个方向推到终点,这个你自己去判一下就好了;
我用了优先队列做优化,原因是人到箱子的四个方向的步数大小不一,因此我们优先选择总步数最小的扩展;
在第二个bfsbfs中,要把箱子当成障碍物;
走过的地方不能再走,但是这里位置的唯一性要由人的位置和箱子的位置共同确定,因此要开一个4维数组,不过我们通过hashhash可以降到2维;
我们把方向按:上 - 0,右 - 1, 下 - 2,左 - 3编号,为的就是在编码的时候可以方便统一地求人要走的那个位置和箱子即将推到的那个位置.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int dirx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
const int diry[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n, m;
struct Point {
int x, y;
Point() {}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
bool operator == (const Point &other) const {
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
};
struct Node {
Point peo, box;
int step;
Node() {}
Node(Point peo, Point box, int step = 0) :
peo(peo), box(box), step(step) {}
bool operator < (const Node &other) const {
return step > other.step;
}
};
struct Peo {
Point point;
int step;
Peo() {}
Peo(Point point, int step = 0) :
point(point), step(step) {}
};
bool check(int x, int y)
{
return x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m;
}
int bfs(Point src, Point des, Point box, vector<string> &mp)
{
queue<Peo> que;
vector<vector<bool> > used(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
que.push(src);
used[src.x][src.y] = true;
int ret = -1;
while (!que.empty()) {
auto now = que.front();
que.pop();
if (now.point == des) {
ret = now.step;
break;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tx = now.point.x + dirx[k];
int ty = now.point.y + diry[k];
if (check(tx, ty) && mp[tx][ty] == '.' && !(Point(tx, ty) == box) && !used[tx][ty])
que.emplace(Point(tx, ty), now.step + 1), used[tx][ty] = true;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("in", "r", stdin);
while (cin >> n >> m) {
string str;
vector<string> mp;
Point initS, initE, initZ;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> str;
mp.push_back(str);
for (int j = 0; j < str.size(); j++) {
if (str[j] == 'S') {
initS = Point(i, j);
mp[i][j] = '.';
break;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < str.size(); j++) {
if (str[j] == 'E') {
initE = Point(i, j);
mp[i][j] = '.';
break;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < str.size(); j++) {
if (str[j] == '0') {
initZ = Point(i, j);
mp[i][j] = '.';
break;
}
}
}
vector<vector<bool> > used(n * m + 1000, vector<bool>(n * m + 1000, false));
priority_queue<Node> que;
que.emplace(initS, initZ);
used[initS.x * n + initS.y][initZ.x * n + initZ.y] = true;
int ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
if (check(initE.x + dirx[k], initE.y + diry[k]) && mp[initE.x + dirx[k]][initE.y + diry[k]] == '.')
++cnt;
while (!que.empty()) {
auto now = que.top();
que.pop();
if (now.box == initE) {
cnt--;
ans = min(now.step, ans);
if (cnt == 0)
break;
else
continue;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tmpSx = now.box.x + dirx[k];
int tmpSy = now.box.y + diry[k];
int tmpZx = now.box.x + dirx[(k + 2) % 4];
int tmpZy = now.box.y + diry[(k + 2) % 4];
if (!check(tmpSx, tmpSy) || !check(tmpZx, tmpZy))
continue;
if (mp[tmpSx][tmpSy] != '.')
continue;
if (mp[tmpZx][tmpZy] != '.')
continue;
if (used[now.box.x * m + now.box.y][tmpZx * m + tmpZy])
continue;
int step = bfs(now.peo, Point(tmpSx, tmpSy), now.box, mp);
if (step == -1)
continue;
que.emplace(now.box, Point(tmpZx, tmpZy), step + now.step + 1);
used[now.box.x * m + now.box.y][tmpZx * m + tmpZy] = true;
}
}
cout << (ans == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : ans) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、房间
题目:
有nn个房间,现在ii号房间里的人需要被重新分配,分配的规则是这样的:先让ii号房间的人全部出来,接下来按照i+1,i+2,i+3,...i+1,i+2,i+3,...的顺序依次往这些房间里放一个人,nn号房间的下一个房间是1号房间,直到所有人被重新分配。
现在告诉你分配完后每个房间的人数以及最后一个人被分配的房间号xx,你需要求出分配前每个房间的人数,数据保证一定有解,若有多解输出任意一个解。
输入描述:
第一行两个整数n,x(2<=n<=105,1<=x<=n)n,x(2<=n<=105,1<=x<=n),代表房间数量以及最后一个人被分配到的房间号;
第二行nn个整数ai(0<=ai<=109)ai(0<=ai<=109),代表每个房间分配后的人数。
样例输入:
3 13 1
6 5 16 5 1
样例输出:
4 4 44 4 4
解析:
首先,如果所有房间都有人,这个问题很好考虑,找最小值,例如最小值是3,长度为4,那么就循环了3圈,然后从最后一个分配到的房间向前数,数到最小值数了多少下。例如样例中,第三个房间的人肯定是被请出去的,那么第三个房间的原本人数就是1×3+1=41×3+1=4,第一个房间的原本人数就是6−1−1=46−1−1=4,第二个房间原本的人数是5−15−1,那么我们就得到了一个一般的解法:先找最小值,然后所有房间的人数先减去最小值,再从最小值这个地方先后到最后一个分配的房间要再减一,最后最小值这个地方的人数就是最小值乘长度加上最后一个人分配的地方向前到这最小值这个地方的距离减一.
但是现在存在有的房间可能没人,这就意味着最小值可能有很多个,那么就要分两种情况了,一、最后一个分配的房间里的人数就是最小值,这种情况这个房间里的人就是先前被请出去了,也就是循环了theMintheMin圈,很好计算;二、最后一个分配的房间里的人数不是最小值,那么先前被请出去的房间就是从最后一个分配的房间向前数第一个遇到的最小值的房间,自己画一个图就理解了.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
int n, k;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &k)) {
vector<LL> arr;
LL theMin = 0x3f3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
LL x;
scanf("%lld", &x);
arr.push_back(x);
theMin = min(theMin, x);
}
if (arr[k - 1] == theMin) {
for (vector<LL>::size_type i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (i == k - 1)
printf("%lld", 1LL * theMin * n);
else
printf("%lld", arr[i] - theMin);
putchar(i == arr.size() - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
} else {
int i, d;
for (i = k - 1, d = 0; theMin != arr[(i + n) % n]; i--, d++)
arr[(i + n) % n] = arr[(i + n) % n] - theMin - 1;
arr[(i + n) % n] = 1LL * theMin * n + d;
if ((i + n) % n != k) {
for (--i; (i + n) % n != k; i--)
arr[(i + n) % n] = arr[(i + n) % n] - theMin;
arr[(i + n) % n] = arr[(i + n) % n] - theMin;
}
for (vector<LL>::size_type i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
printf("%lld%c", arr[i], i == arr.size() - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
return 0;
}
3、(附加题)二阶魔方
题目:
二阶魔方又叫小魔方,是2*2*2的立方体结构,每一面都有4个块,共有24个块,每次操作可以将一面逆时针或者顺时针旋转90。90。,如将上面逆时针旋转90。90。操作如下:
这里写图片描述

Zero在小魔上做了一些改动,用数字替换每个块上面的颜色,称之为数字魔方。魔方上每一面的优美度就是这个面上4个数字的乘积,而魔方的总优美度就是6个面优美度的总和。
现在Nero有一个数字魔方,他想知道这个魔方在操作步超过5次的前提下能达到的最大优美度是多少。
魔方展开后每一块的序号如下图:
这里写图片描述
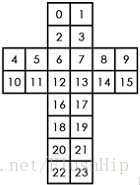
输入描述:
输入一行包含24个数字,按序号顺序给出魔方每一块上面的数字。所有数字的范围为[−100,100][−100,100]。
输出描述:
输出一行包括一个数字,表示最大优美度。
样例输入:
2 −3 −2 3 7 −6 −6 −7 9 −5 −9 −3 −2 1 4 −9 −1 −10 −5 −5 −10 −4 8 22 −3 −2 3 7 −6 −6 −7 9 −5 −9 −3 −2 1 4 −9 −1 −10 −5 −5 −10 −4 8 2
样例输出:
82818281
解析:
模拟题,最主要的是写出6个移动位置的置换群,仔细点写,我一开始写错好几次,太多了,本来想用代码来写,但是想了下,还不如手写呢,最后我是通过下面这个debug函数才找出来我哪个地方写错了,如果这个函数输出的全是1,那么数字上就没错,但是不保证你的置换方式有没有错.
void debug()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int a[24];
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
cout << i << ":" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 24; j++)
a[mp[i][j]]++;
for (int j = 0; j < 24; j++)
printf("%d ", a[j]);
puts("");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
还要注意一点,这里顺时针逆时针只要考虑一个就好了,因为顺时针移动三次可以得到逆时针!
时间复杂度O(125)O(125)可以接受,不过这个题如果说在15步内那就不是这么简单的了,首先,15步去暴搜是不行的,太多了,那么怎么办呢,这个时候我们就要考虑魔方的“上帝之数”了,二阶魔方在任意状态11步内是可以还原的,那么也就是说,15步可以从任意一个状态到另一个任意的状态了,那么这个问题就变成了,24个数字分成6组,求这6个组的乘积最大和了,但是要注意一点,有些数字是永远不可能出现在同一面的,这个要考虑到,比如一条棱上的两个数字。
这样子考虑不用去模拟魔方转动了,但是好像这个问题变难了,贪心是肯定搞不了的,我也不知道做了.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mp[6][24] = {
// {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23},
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 21, 20, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 16, 19, 17, 15, 14, 22, 23},
{1, 3, 0, 2, 23, 22, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 9, 8},
{0, 21, 2, 23, 4, 5, 6, 1, 9, 15, 10, 11, 12, 3, 8, 14, 16, 7, 18, 13, 20, 17, 22, 19},
{20, 1, 22, 3, 10, 4, 0, 7, 8, 9, 11, 5, 2, 13, 14, 15, 6, 17, 12, 19, 16, 21, 18, 23},
{0, 1, 11, 5, 4, 16, 12, 6, 2, 9, 10, 17, 13, 7, 3, 15, 14, 8, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23},
{10, 4, 2, 3, 18, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0, 19, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1, 16, 17, 15, 9, 21, 23, 20, 22}
};
const int face[6][4] = {
{0, 1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 10, 11},
{6, 7, 12, 13},
{8, 9, 14, 15},
{16, 17, 18, 19},
{20, 21, 22, 23}
};
LL ans;
void flip(vector<int> &a, int index)
{
vector<int> b(a);
for (vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
b[i] = a[mp[index][i]];
a = b;
}
LL getSum(vector<int> &arr)
{
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
LL s = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
s *= arr[face[i][j]];
ret += s;
}
return ret;
}
void dfs(int dep, vector<int> arr)
{
ans = max(ans, getSum(arr));
if (dep == 5) {
return ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
vector<int> a(arr);
flip(a, i);
dfs(dep + 1, a);
flip(a, i);
flip(a, i);
dfs(dep + 1, a);
}
}
void debug()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int a[24];
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
cout << i << ":" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 24; j++)
a[mp[i][j]]++;
for (int j = 0; j < 24; j++)
printf("%d ", a[j]);
puts("");
}
}
int main()
{
// debug();
// freopen("in1", "r", stdin);
while (true) {
bool isBreak = true;
vector<int> arr(24);
for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++)
if (cin >> arr[i])
isBreak = false;
else
break;
if (isBreak)
break;
ans = -0x3f3f3f3f3f;
dfs(0, arr);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}

